Reflexive Relation
A relation R on a set A is said to be reflexive if every element of A is related to itself.
Thus, \epsilon&space;R\&space;\forall\&space;a\epsilon&space;A&space;\right&space;\}) .
.
Note : A relation is not reflexive if their exists an element such that (a,a)∉R .
such that (a,a)∉R .
,(2,2),(3,3),(1,3),(2,1)&space;\right&space;\}) is a reflexive relation on A.
is a reflexive relation on A.
but,,(3,3),(2,1),(3,2)&space;\right&space;\}) is not a reflexive relation on A ,
is not a reflexive relation on A ,
because 2 ∈ A but (2,2) ∉ R .
Note : For reflexive relation doublet of every element of a given set should be present .
Symmetric Relation
A relation R on a set A is said to be symmetric relation if (a,b)∈R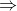 (b,a)∈R
(b,a)∈R 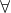 (a,b)∈A
(a,b)∈A
i.e. aRb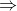 bRa for all a , b ∈ A .
bRa for all a , b ∈ A .
For example : Let A = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } and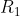 and
and 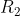 be relations on A given by
be relations on A given by
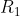 = { (1,3) , (1,4) , (3,1) , (2,2) , (4,1) }
= { (1,3) , (1,4) , (3,1) , (2,2) , (4,1) }
and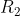 = { (1,1) , (2,2) , (3,3) , (1,3) }
= { (1,1) , (2,2) , (3,3) , (1,3) }
In above relations :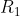 is symmetric on A because (a,b) ∈
is symmetric on A because (a,b) ∈ 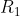
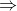 (b,a) ∈
(b,a) ∈ 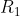
but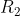 is not symmetric on A because (1,3) ∈
is not symmetric on A because (1,3) ∈ 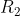 but (3,1) ∉
but (3,1) ∉ 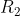 .
.
Note : A reflexive relation on a set A is not necessarily symmetric.
e.g: the relation R = {(1,1),(2,2),(3,3),(1,3)} is a reflexive on set A = {1,2,3}
but it is not symmetric.
Transitive Relation
Let A be any set. A relation R on A is said to be transitive relation if
(a,b) ∈ R and (b,c) ∈ R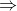 (a,c) ∈ R for all a,b,c ∈ A .
(a,c) ∈ R for all a,b,c ∈ A .
i.e., aRb and bRc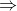 aRc for all a,b,c ∈ A .
aRc for all a,b,c ∈ A .
For example : On the set N of natural numbers, the relation R defined by xRy .
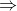 'x is less than y' , is transitive , because for any x,y,z ∈ N
'x is less than y' , is transitive , because for any x,y,z ∈ N
x < y and y < z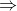 x < z
x < z
i.e., xRy and yRz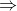 xRz
xRz
Note : A relation is not reflexive if their exists an element
For example : Let A = { 1 , 2 , 3 } be a set. Then
but,
because 2 ∈ A but (2,2) ∉ R .
Note : For reflexive relation doublet of every element of a given set should be present .
Symmetric Relation
A relation R on a set A is said to be symmetric relation if (a,b)∈R
i.e. aRb
For example : Let A = { 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 } and
and
In above relations :
but
Note : A reflexive relation on a set A is not necessarily symmetric.
e.g: the relation R = {(1,1),(2,2),(3,3),(1,3)} is a reflexive on set A = {1,2,3}
but it is not symmetric.
Transitive Relation
Let A be any set. A relation R on A is said to be transitive relation if
(a,b) ∈ R and (b,c) ∈ R
i.e., aRb and bRc
For example : On the set N of natural numbers, the relation R defined by xRy .
x < y and y < z
i.e., xRy and yRz

Comments
Post a Comment